Introduction
🔰 What is Portainer?
Portainer is an open source, lightweight management UI that allows us to easily build and manage containers in Docker, Docker Swarm, Kubernetes and Azure ACI such as managing the creation and deletion of Swarm services, user authentication, authorizations, connecting, executing commands in the console of running containers, and viewing containers’ logs.
Portainer consists of a single container that can run on any cluster. It can be deployed as a Linux container or a Windows native container.
It is the most widely adopted container management platform in the world, with over 650,000 users and 21,700 stars on GitHub.
🔰 Why Portainer 🤔
✅ Portainer removes the complexity associated with deploying and managing containers
Portainer’s goal is to deliver a world class container-native application deployment and Management tool that is truly platform agnostic. To achieve this, they have made the underlying container management platform (eg, Kubernetes) invisible to the engineers who simply want to manage their apps. If you use Portainer we’re able to CONSUME the container platform without being an expert in it.
✅ Portainer streamlines the operations of container management
With Portainer, engineers can deploy and see the state of individual containers, restart them and debug them when necessary – all without needing to use the command line. Portainer also provides deep visibility into what’s running, where it's running and how it's running, which helps engineers optimize app performance.
And because Portainer connects to all your hosts and platforms, you get full visibility on a single webpage, which eliminates the need to connect to each individual container to check on its state. This saves masses of time time and lets engineers focus on what’s important.
✅ Portainer provides an enterprise sensitive tool that complies with IT governance best practice
Technology leaders need to be able to manage apps in a secure, repeatable, and scalable manner. Portainer provides a structured framework for that enables this to happen as well as enabling teams to work collaboratively. This reduces risk on your business and helps you be compliant in the way you deploy and manage your applications.
Identity and Access management is a problem in native container platform management and it’s a problem Portainer solves. It gives you the ability to assign specific roles with pre-set functionality limits to users and teams and even nest roles to create fine grained access rights.
And also Portainer automatically logs all actions taken around container management, capturing details on who created, maintained, or even deleted containers – helping you trace back any issues that might occur across your organization.
Portainer Architecture
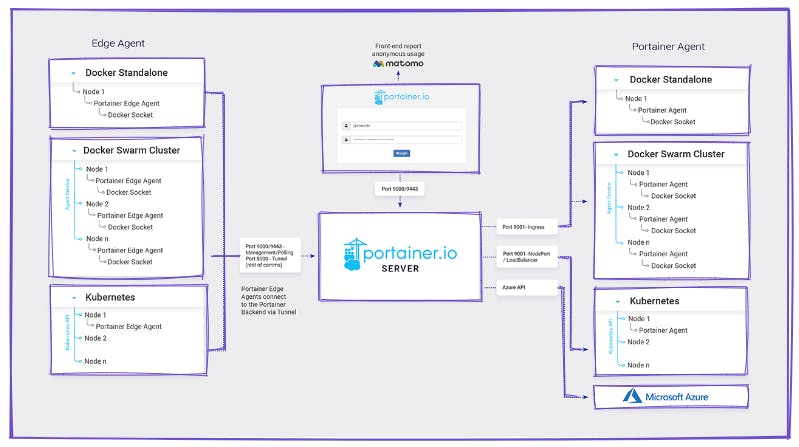
Portainer consists of two elements: the Portainer Server and the Portainer Agent.
Both Portainer Server and Portainer Agent run as lightweight containers on your existing containerized infrastructure.
The Portainer Agent should be deployed to each node in your cluster and configured to report back to the Portainer Server container. A single Portainer Server will accept connections from any number of Portainer Agents, providing the ability to manage multiple clusters from one centralized interface. To do this, the Portainer Server container requires data persistence.
The Portainer Agents are stateless, with data being shipped back to the Portainer Server container.
Features Of Portainer
Application Deployment - Manage the deployment of containerized applications through a manual GUI or Simple GitOps.
Observability & Triage - Monitor the performance and behaviour of containerized applications.
Centralized IAM - Control who can do what, when and why inside your environment.
Platform Management - Set up and configure your environment - on-prem, in the cloud or at the edge.
Portainer Products
Portainer is available in two versions: Community Edition (CE) and Business Edition (BE).
💥 Portainer CE
It is an open source software intended for personal use and supported by a vibrant and growing community users.
Portainer Community Edition (CE) is the foundation. With over half a million regular users, CE is a powerful, open source toolset that allows you to easily build and manage containers in Docker, Docker Swarm, Kubernetes and Azure ACI.
💥 Portainer BE
It is a commercially licensed and supported product that adds enterprise features to CE to support enterprise requirements and is intended for professional use.
Portainer Business Edition (BE) is the commercial offering. With features geared towards businesses and larger organizations such as Role-Based Access Control, registry management, and dedicated support, Portainer BE is a powerful toolset that allows you to easily build and manage containers in Docker, Docker Swarm, Kubernetes and Azure ACI.
Installation
Check out the Official Documentation for Portainer Installation according to your requirements.
💥 In this blog I will be using helm to install Portainer.
🔰 Prerequisites
- A working and up to date Kubernetes cluster.
- Access to run helm or kubectl commands on your cluster.
- Cluster Admin rights on your Kubernetes cluster. This is so Portainer can create the necessary ServiceAccount and ClusterRoleBinding for it to access the Kubernetes cluster.
- A default StorageClass configured.
So, Let's get started 🚀🥳
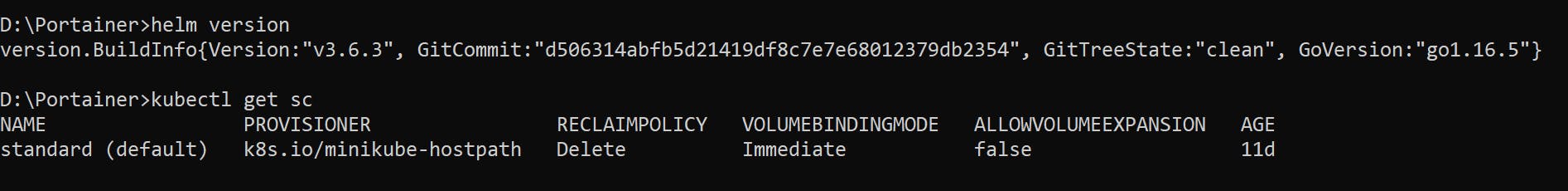
👉 Check if you have a default StorageClass by running the following command on your cluster:
kubectl get sc
📌 If the storage class is not set as default then we can use the below command to set a default storage class.
kubectl patch storageclass <storage-class-name> -p '{"metadata": {"annotations":{"storageclass.kubernetes.io/is-default-class":"true"}}}'
📌 replacing with the name of your StorageClass. Alternatively, if you are installing using our Helm chart, you can pass the following parameter in your helm install command to specify the StorageClass to use for Portainer:
--set persistence.storageClass=<storage-class-name>
📌 In my case, it's already set as default.
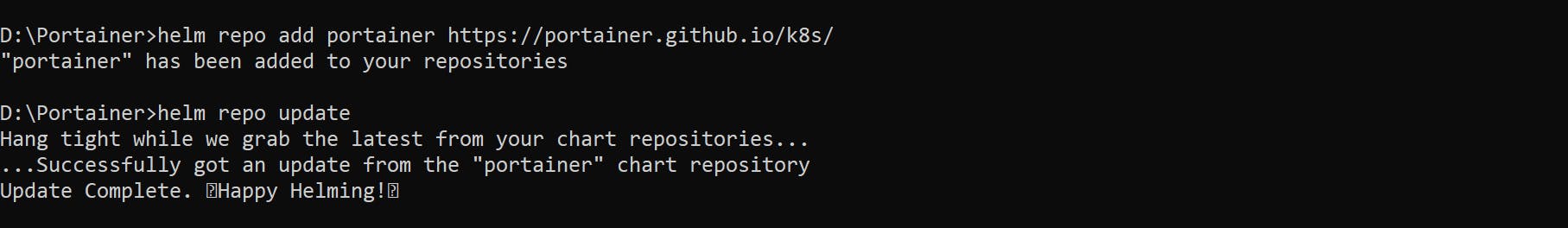
👉 Now, add the Portainer Helm repository by running the following commands:
helm repo add portainer https://portainer.github.io/k8s/
helm repo update
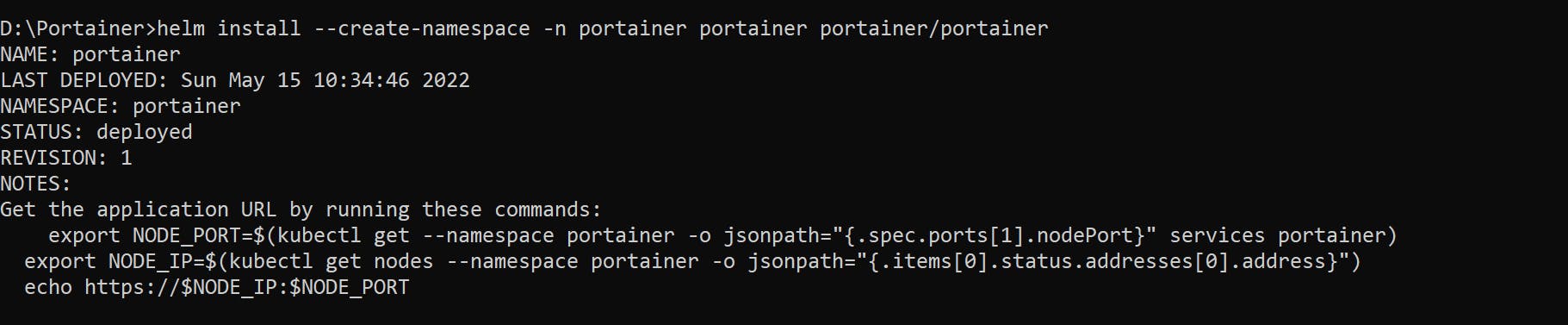
👉 Install the helm chart:
helm install --create-namespace -n portainer portainer portainer/portainer
👉 Check the service
kubectl get svc -n portainer
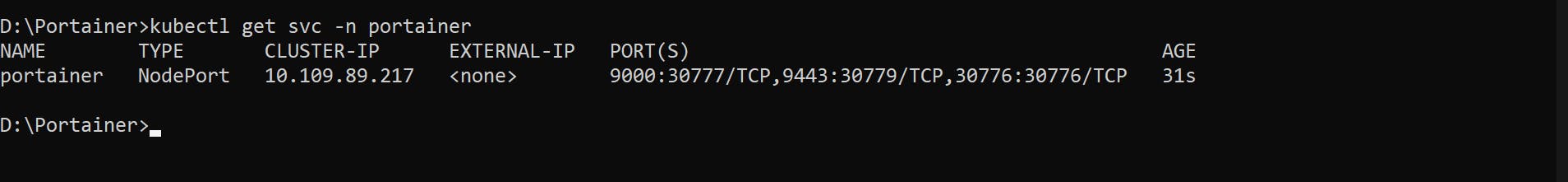
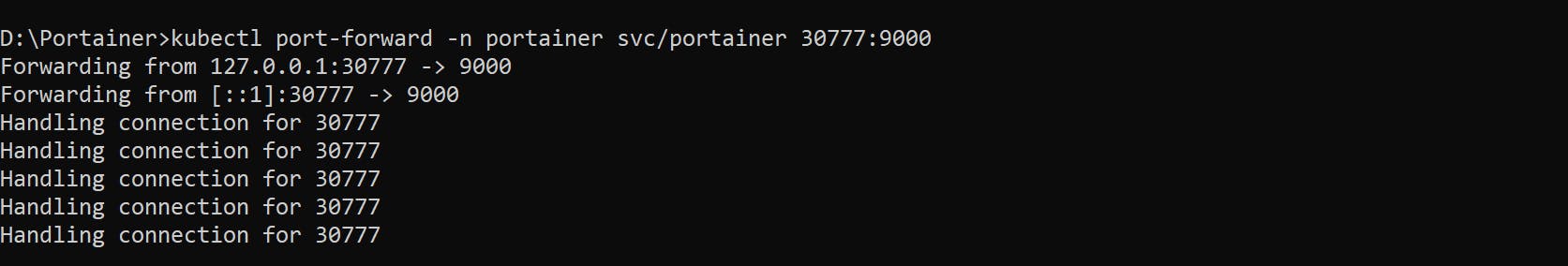
👉 To access the portainer service from the local environment on port 30777, Traffic can be forwarded to your local system using the port-forward command:
kubectl port-forward -n portainer svc/portainer 30777:9000
👉 Open a web browser and navigate to the following URL:
http://localhost:30777 or http://localhost:30779/ or http://localhost:30776/

📌 Now, set the username and password then click on create user

📌 Click on Get started
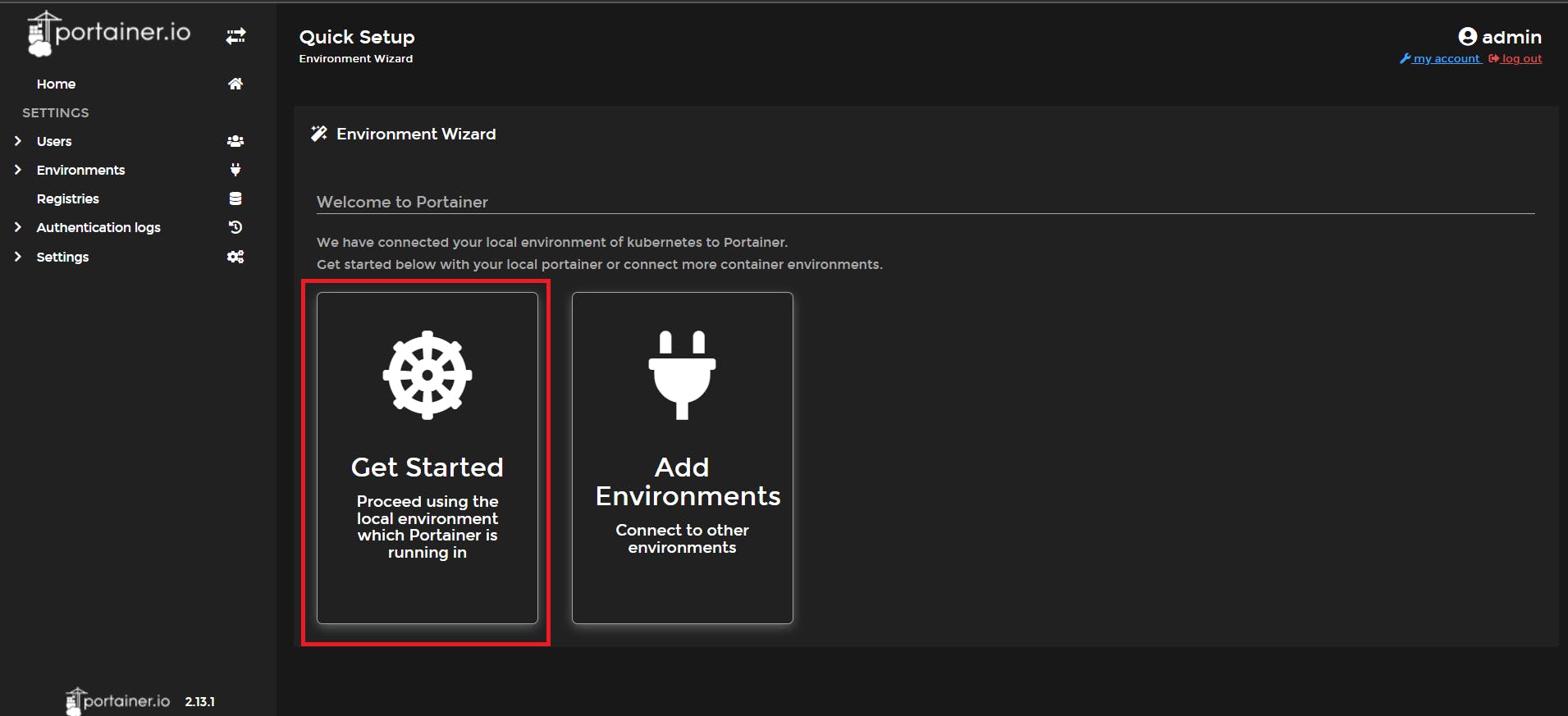
Now , we are all set to explore the Portainer UI 🥳
🔰 Choose our environment and then we will land to the dashboard from where we can manage the cluster.
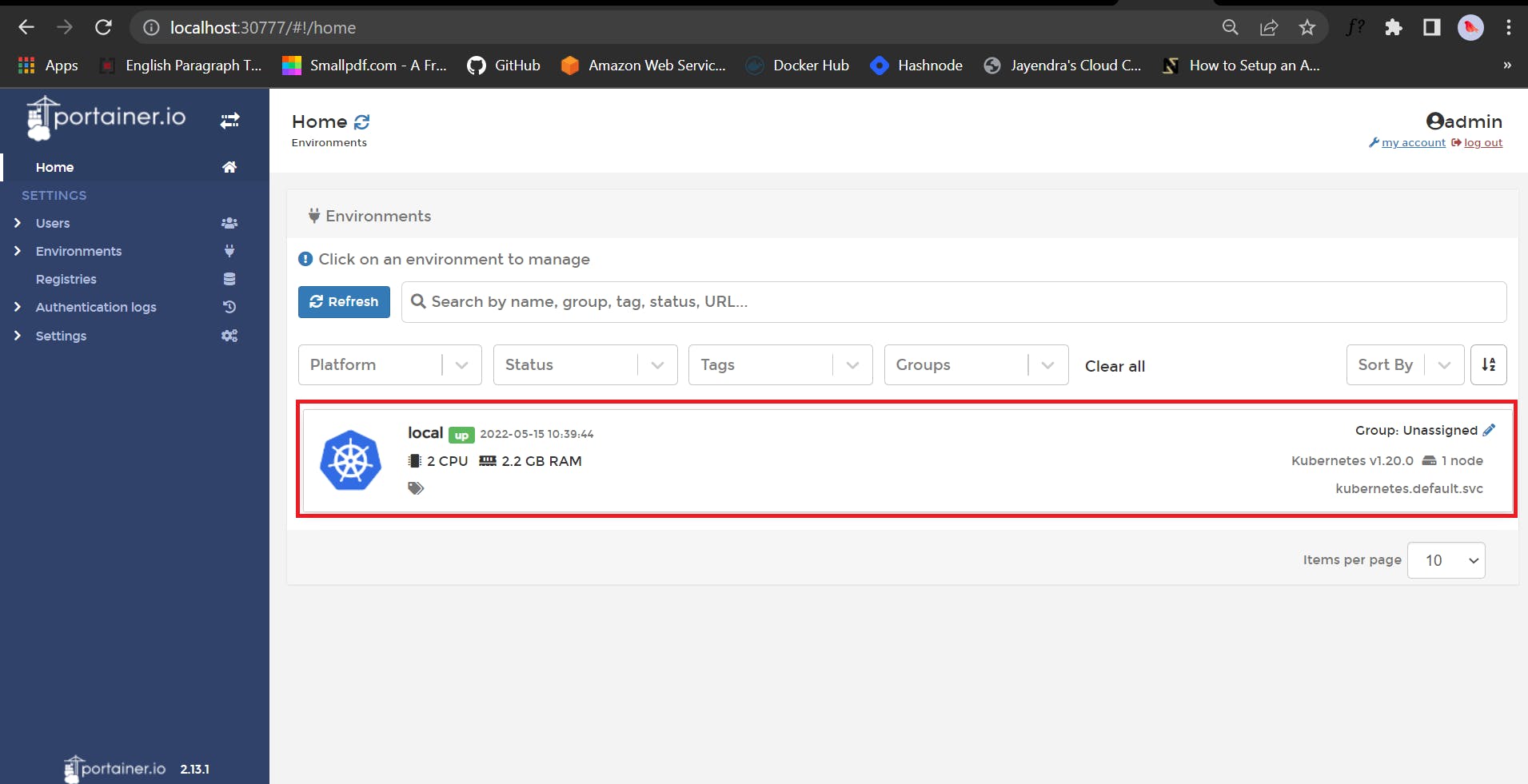
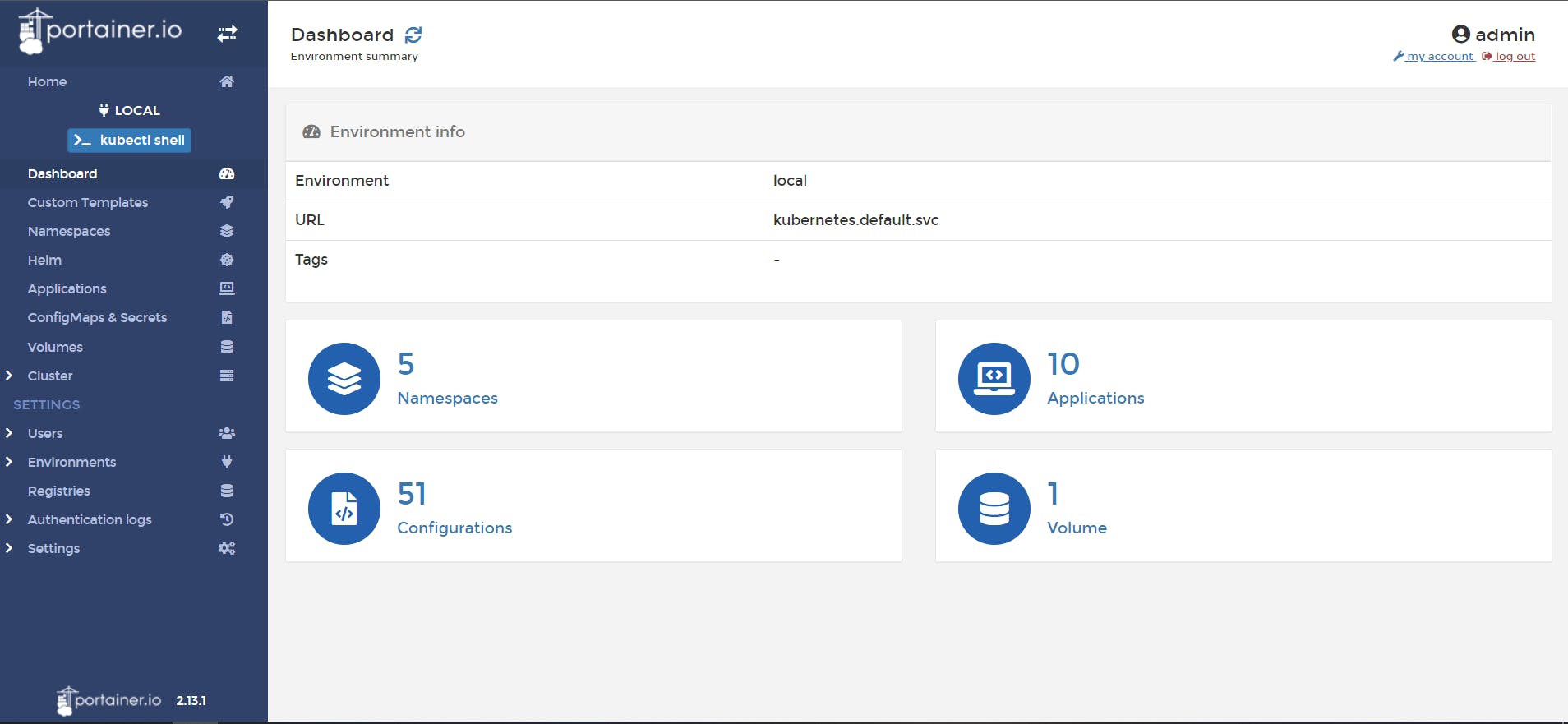
Now, Let's do some hands-on practical 🚀
📌 Click on the Namespace , you will see the default Namespace
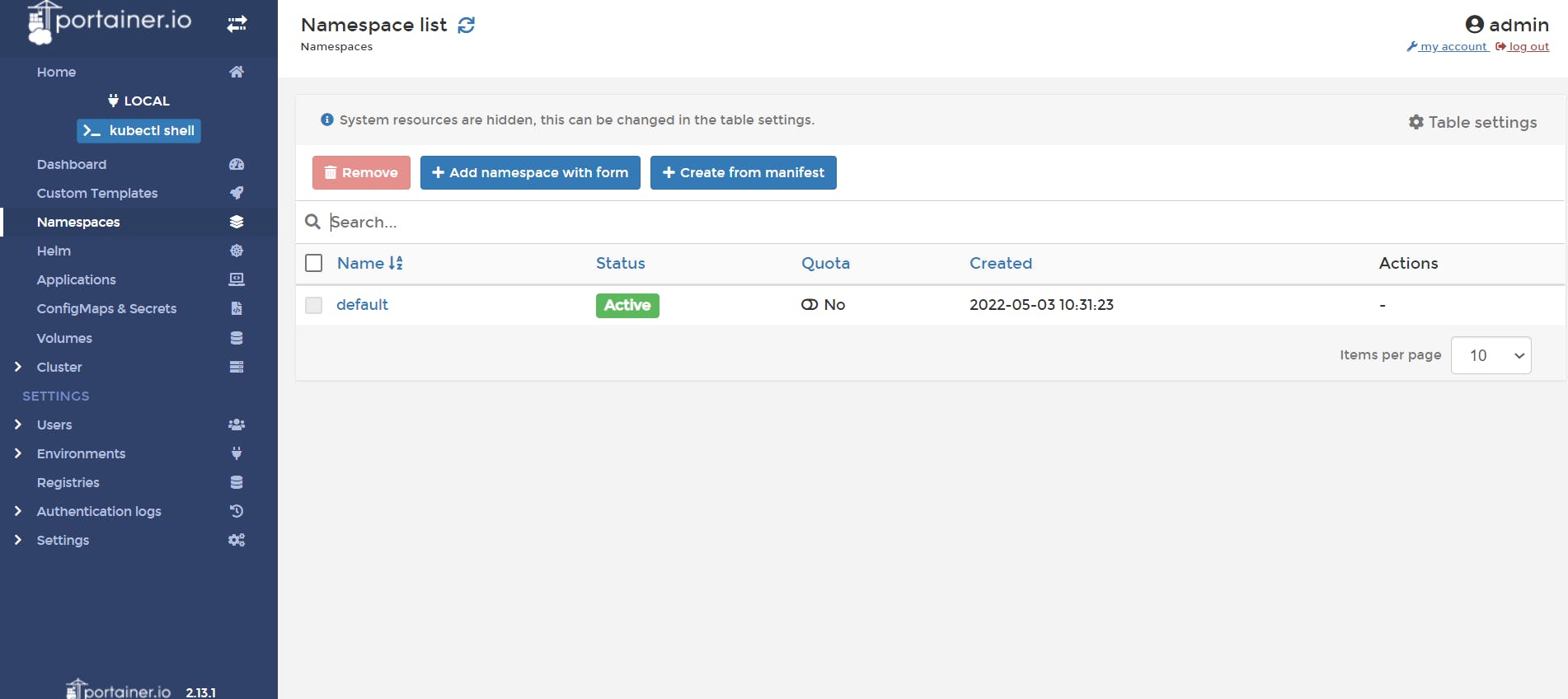
📌 Click on Add Namespace with form
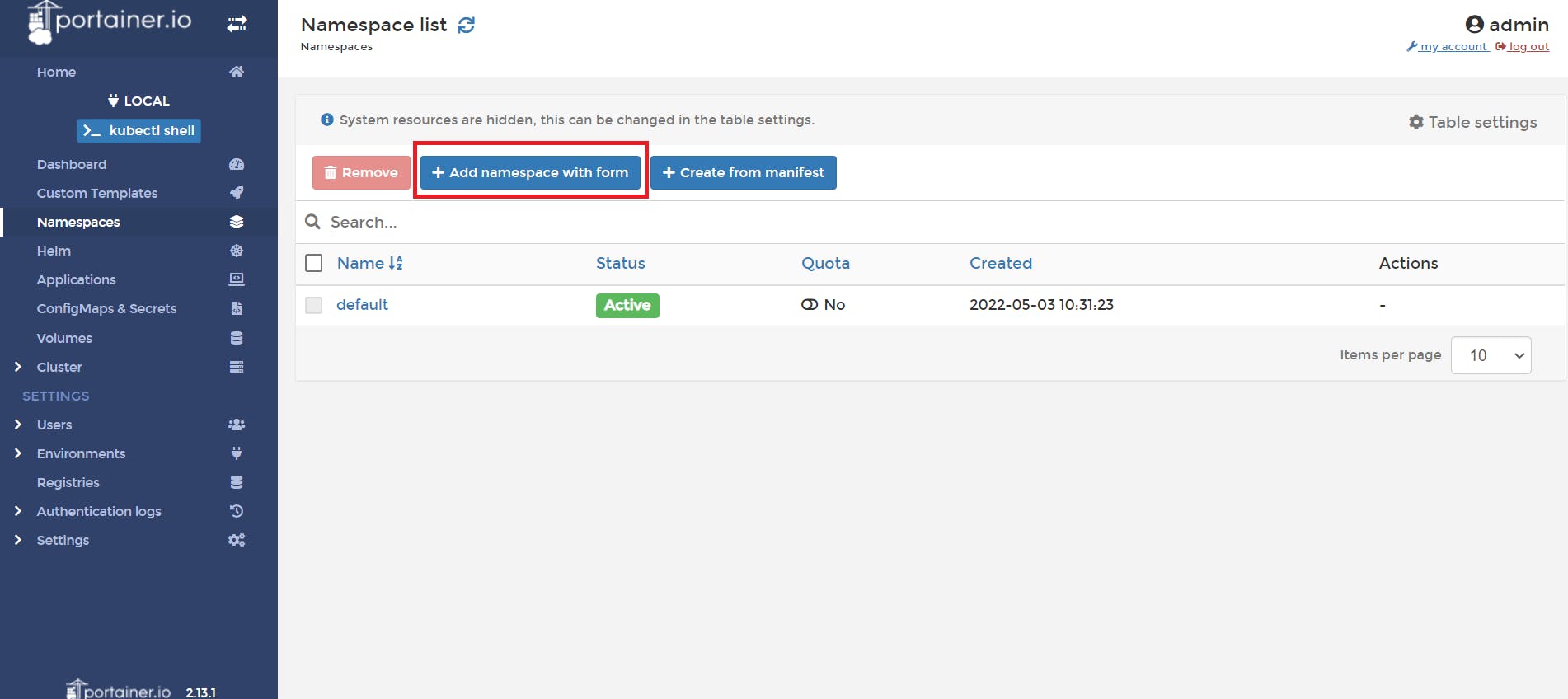
📌 Give the name , set the memory and CPU usage , then click on create namespace
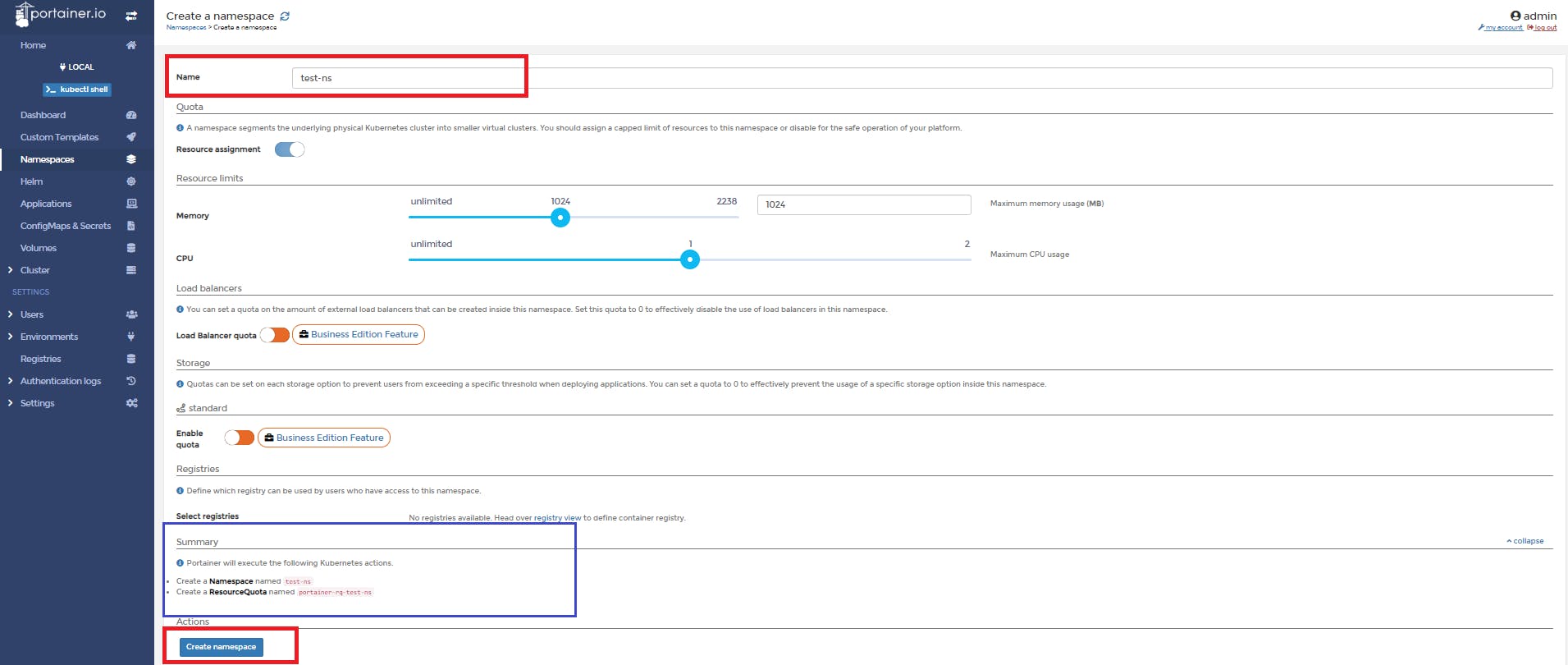
📌 Let's see the namespace list
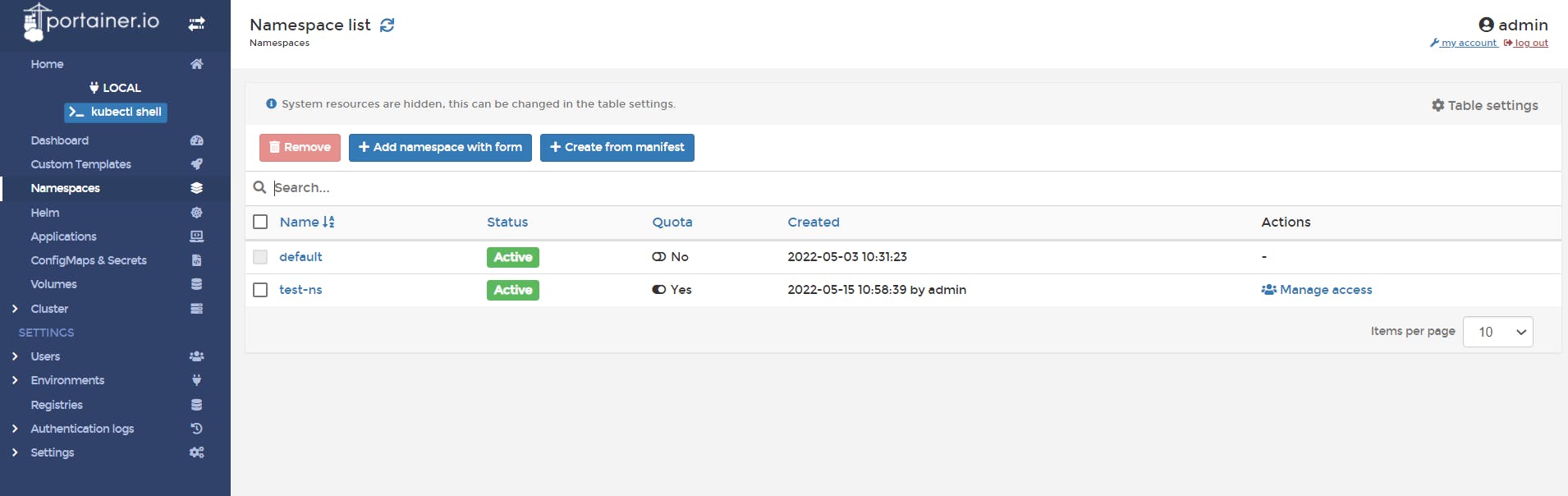
So, we have successfully create our namespace 🤩
👉Now. Let's create an application in our own namespace that we created above.
📌 Click on Application
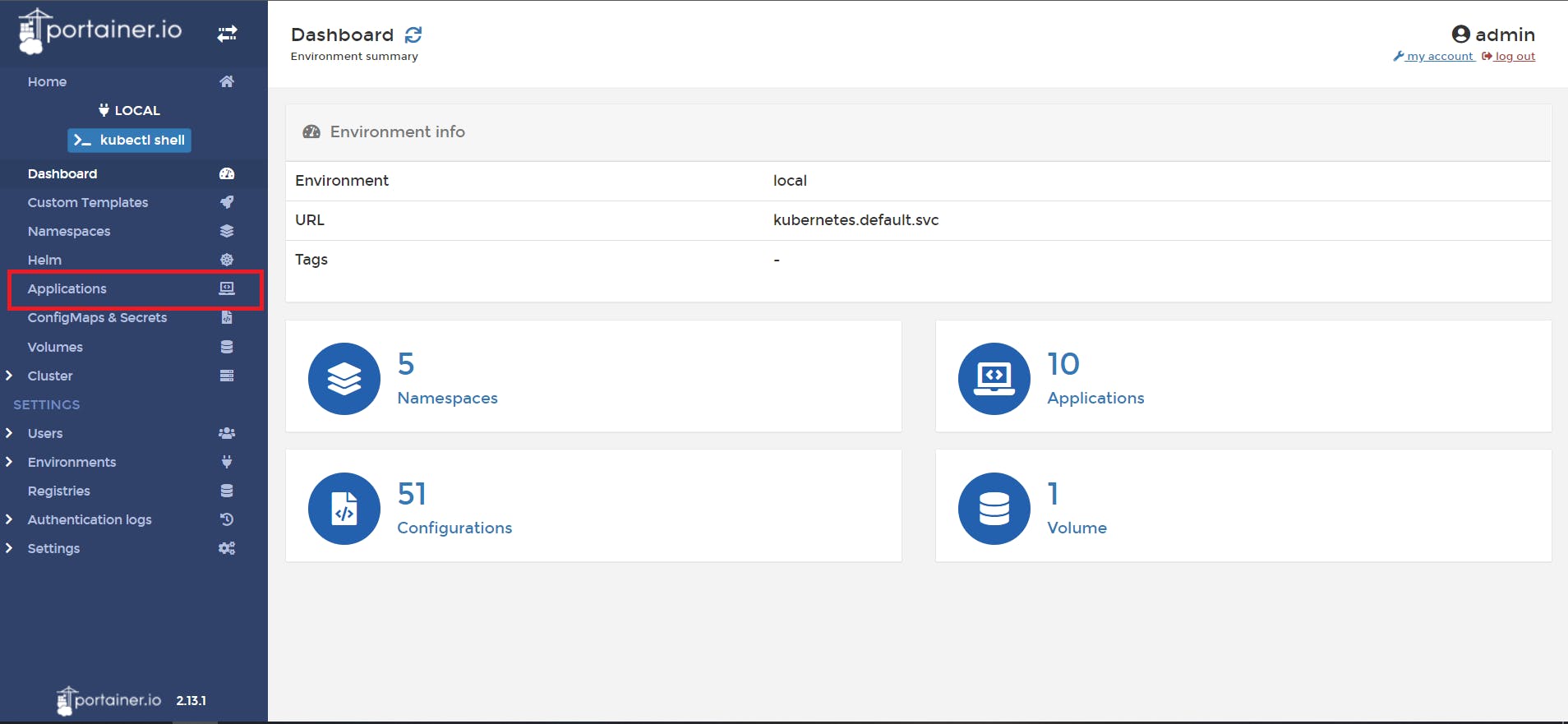
📌 click on Add application with form
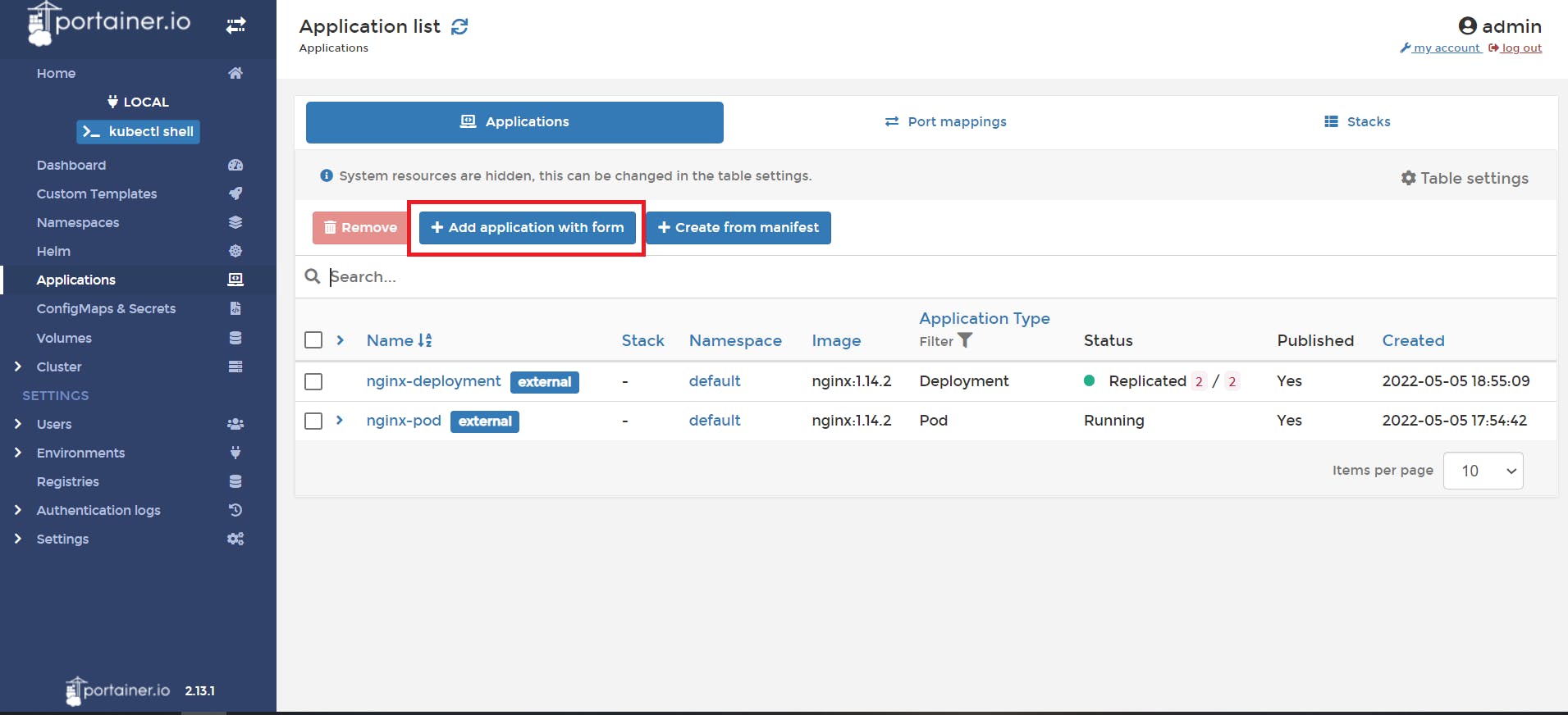
📌 Select the namespace we created from dropdown, Give the application name, image name, and select service type.
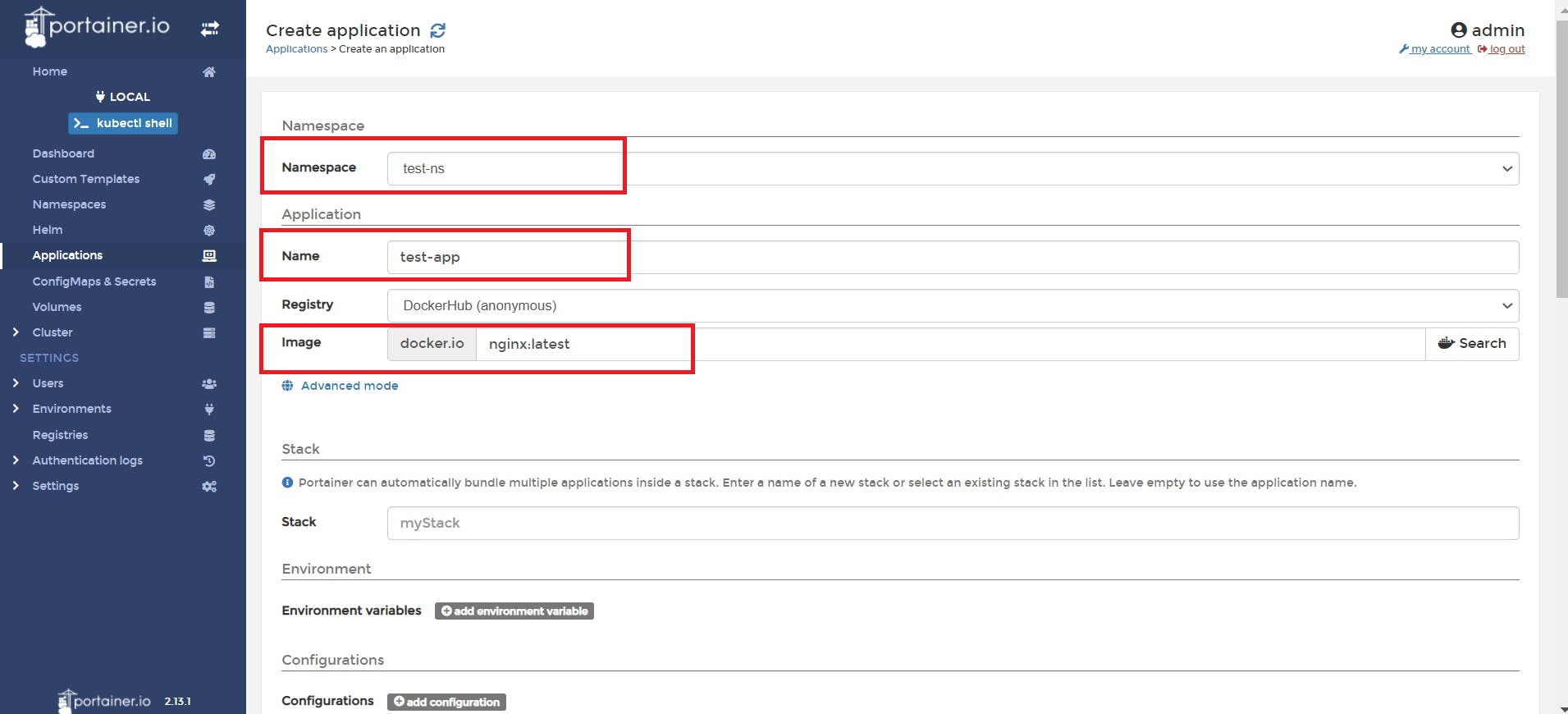
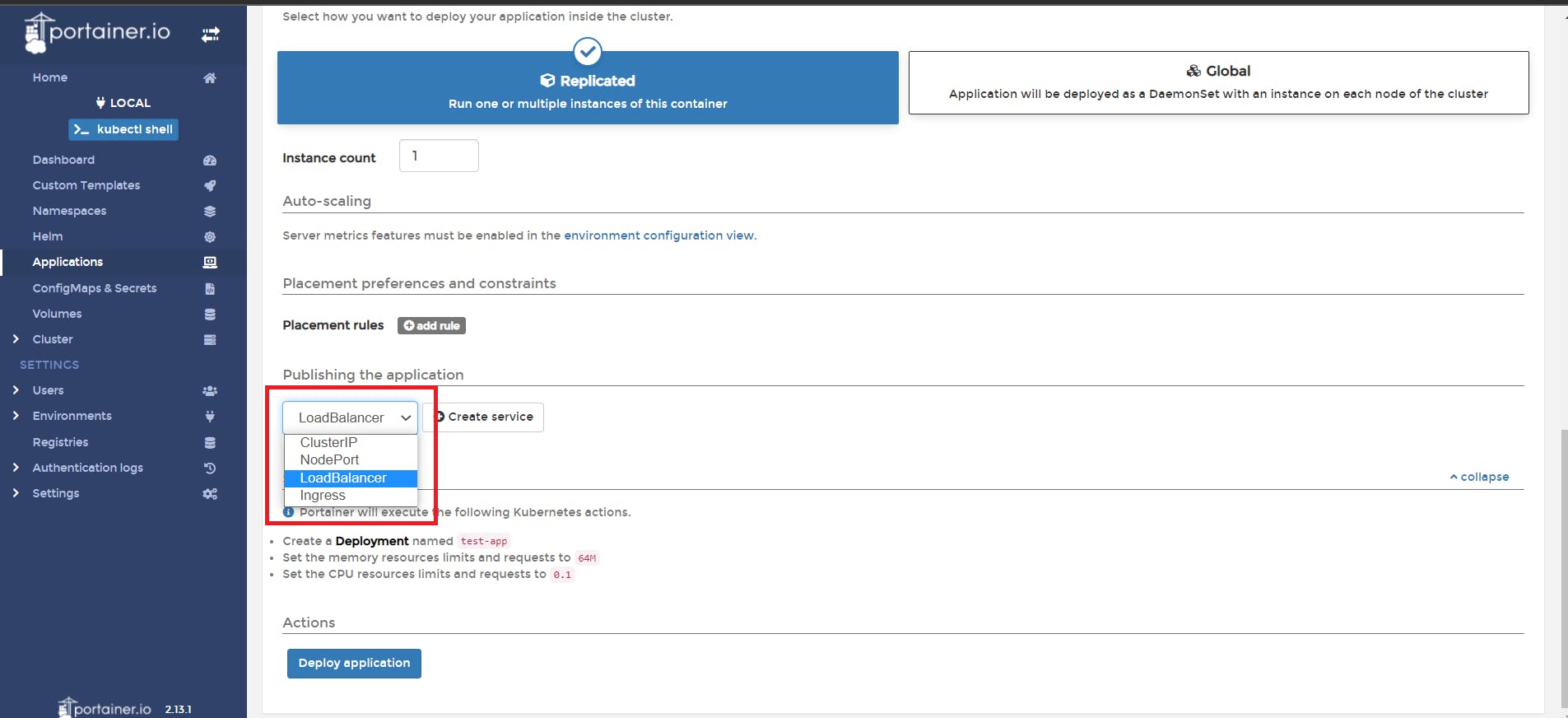
📌 Let's see the application list
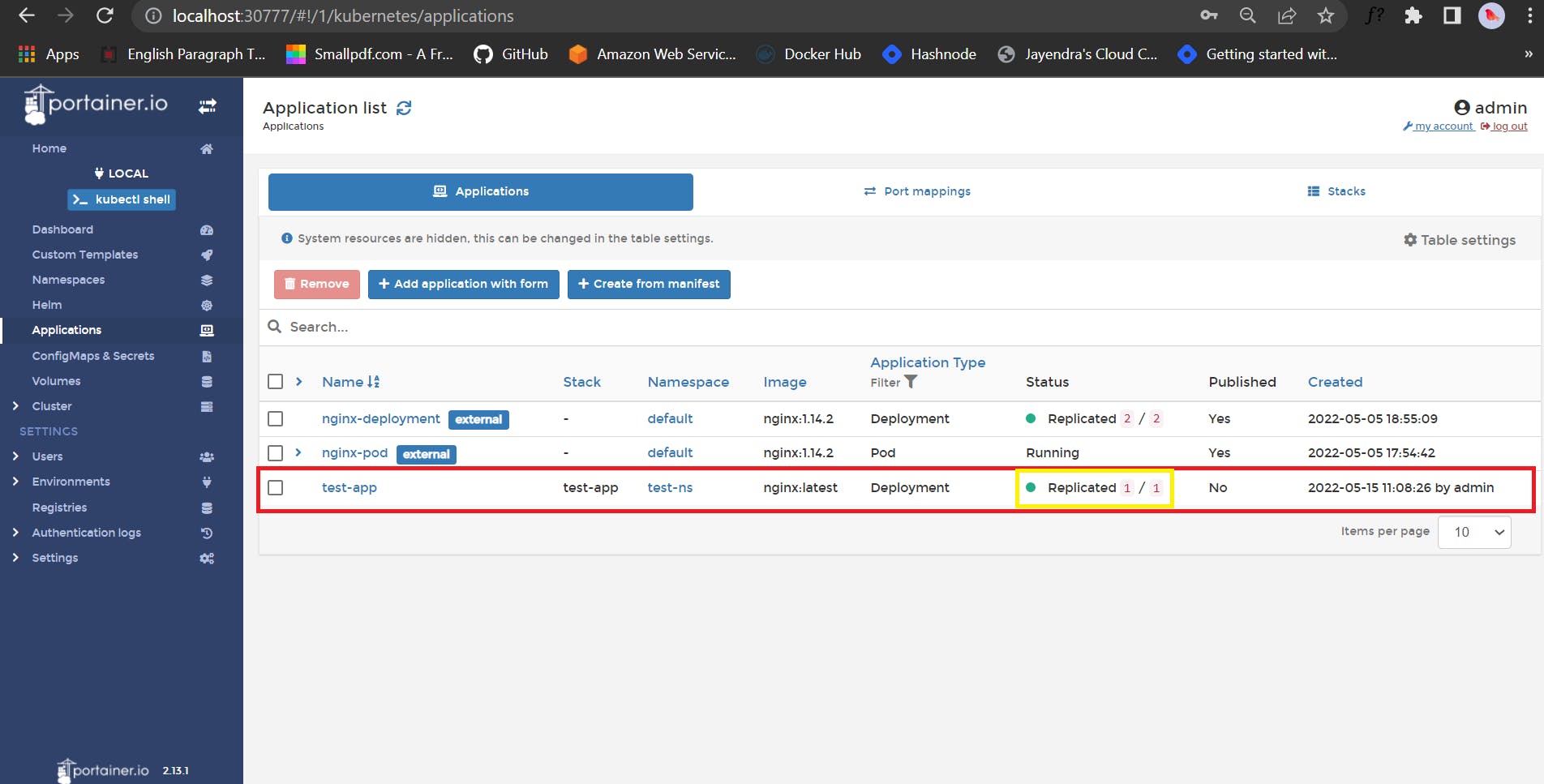
Wooooh, we have successfully created our application 🥳
Conclusion
Portainer is a great tool that can be used to manage Docker containers, Swarm services, and other resources from a simple and intuitive web user interface. Portainer provides several free features and paid plugins that can enhance the user experience for managing Docker clusters. On the other hand, some of the paid plugins still have some restrictions or missing features that could improve the product.
💥 I hope this blog will help you all in understanding how Portainer manages containers.
THANKS FOR READING !!
🔰KEEP LEARNING !! KEEP SHARING 🧾🔰
🚀 Feel free to connect with me :

